Preliminary Design
Requested by: Mr. Ken Swarner
Systems Administrator
Computer Science Department of
Siena College
TCP/IP Packet Descriptor
Mirage Incorporated
“We are there…even if you cannot see us”
Mirageinc2003@yahoo.com
Prepared by: Paul Aiuto
Richard Connell
Lauren Englisbe, Team Leader
Jayme Gresen
Jeffrey Habiniak
December 5, 2003
Preliminary Design
Table
of Contents
|
1.0 External Design Specifications
|
3
|
|
1.1
User Displays
|
3-12
|
|
1.2
User Command Summary
|
13
|
|
1.3
Detailed Data Flow Diagrams
|
14-16
|
|
1.4
Hardware, Software, and Human Interfaces
|
17
|
|
2.0 Architectural Design Specification
|
18
|
|
2.1
User Commands (AKA “Clickable Buttons”)
|
18
|
|
2.2
Functional Descriptions
|
19
|
|
2.2.1
IP PDU for the selected FTP PDU
|
19-32
|
|
2.2.2
TCP PDU for the selected FTP PDU
|
33-43
|
|
2.2.3
FTP PDU for the selected FTP PDU
|
44
|
|
2.2.4
IP PDU for the selected ICMP PDU
|
45-57
|
|
2.2.5
ICMP PDU for the selected ICMP PDU
|
58-64
|
|
3.0 Appendix
|
65
|
|
3.1
Glossary
|
65-67
|
|
3.2
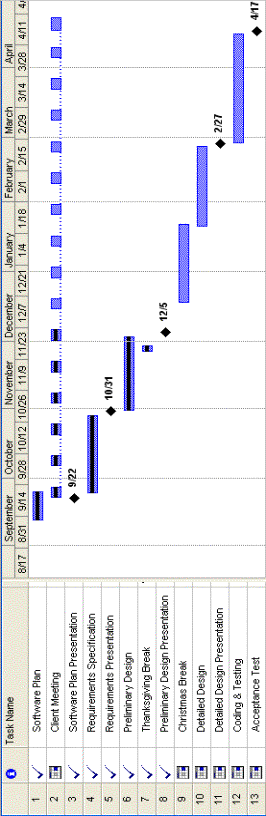
Gantt Chart
|
68-69
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 External Design Specifications
1.1
User displays

This will be the first screen the
user sees. It is the introduction
screen to our software, and presents our mascot, “The Descript-roar”.
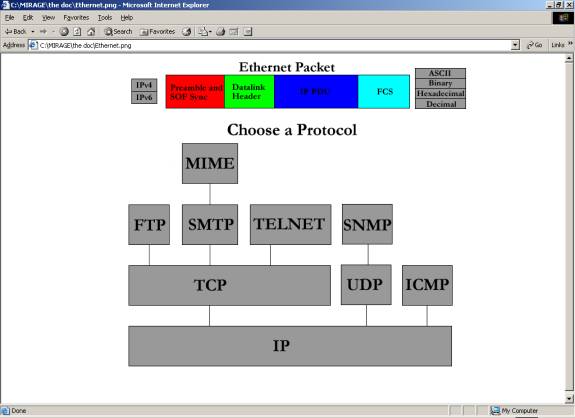
This is the first functional screen
the user will see. It allows the user
to see what an Ethernet Packet looks like, and eventually each frame within
that packet will be clickable and able to display information about that frame.
The “Choose
a Protocol” menu gives the user a graphical representation of how protocols are
interrelated, and allows the desired protocol to be selected.
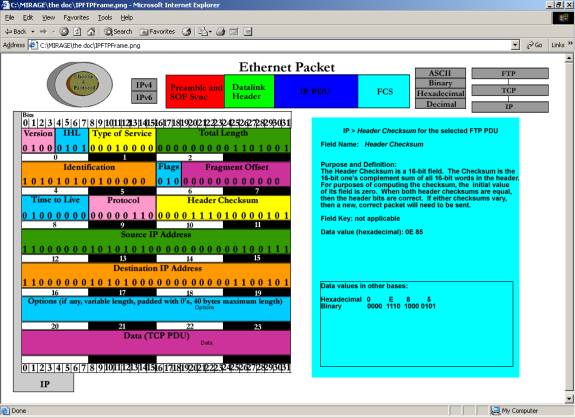
Once a
protocol has been selected by the user, this screen will display. The basis for our protocol suite, the IP PDU
is displayed on the left, filled in with the given data for the selected
protocol. The user is able to click on
any field in the IP PDU, and an information box will display on the right,
describing that field. In the IP PDU
Data field, “TCP PDU” is written – this indicates that the entire TCP PDU is
contained within the IP Data field. If
the user clicks on this field, the TCP PDU will be displayed.
The PDUs are tabbed on their lower left corners:
this allows the user to navigate between them.
Additionally, there is a key at the top right corner to display what
PDUs make up the chosen protocol. The
user may also click on any PDU in this map to navigate. If at any point, the user wants to choose a
different protocol to view, he or she may click on the “Choose a Protocol”
button in the top left corner.
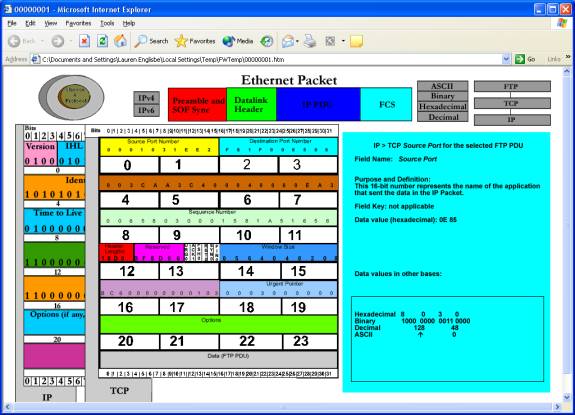
The next screen shows the TCP PDU on top of the IP
PDU. This is meant to show that the TCP
PDU is contained within the IP PDU.
Additionally, the FTP PDU is contained within the TCP PDU Data field, so
clicking on that field will display the FTP PDU. As with IP, if a TCP field is clicked, the information for that
field will be displayed in the information box at the right.
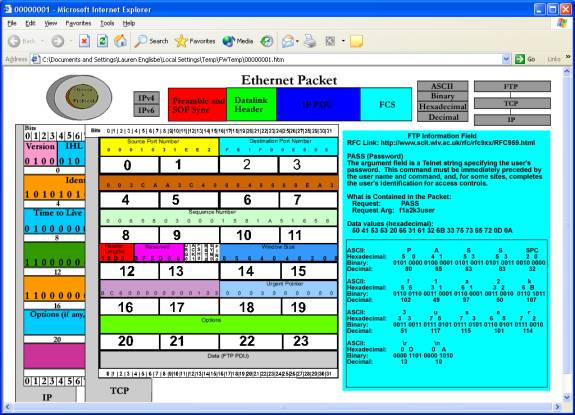
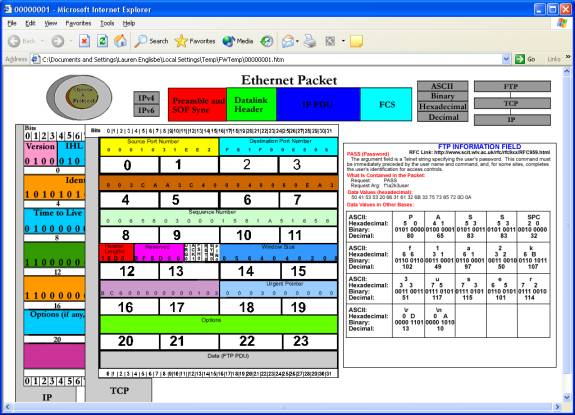
This is the software with all the
information displayed for the selected FTP PDU. The IP PDU gives rise to the TCP PDU, and the TCP Data field has
been clicked, which allows us to see the information field for the FTP PDU on
the right.
Mirage has provided a number of
prototype options, which will be chosen by the client at a later date.
Prototype Model Option 1 (IP PDU):
Prototype Model Option 2 (TCP PDU):
We also have two choices to allow for information display
for a given field.
Information Field Option 1:

Information Field Option 2:
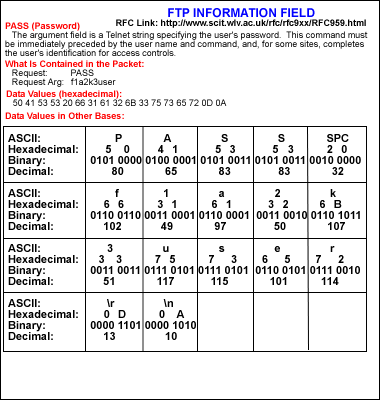
This is the user display using our second option for the
Information Field:
1.2 User Command Summary
Main Screen
This is the screen giving the user the option to choose many
different packets.
PDU Hierarchy Tree
Allows the user to see their progression through the many
packets, and also able to choose their desired packet.
IP Version
Allows the user two chooses of two different IP Versions.
Radix (Base) Selection
Allows the user to select a radix to display.
Information Box
Allows the user to see the given information for a selected
field.
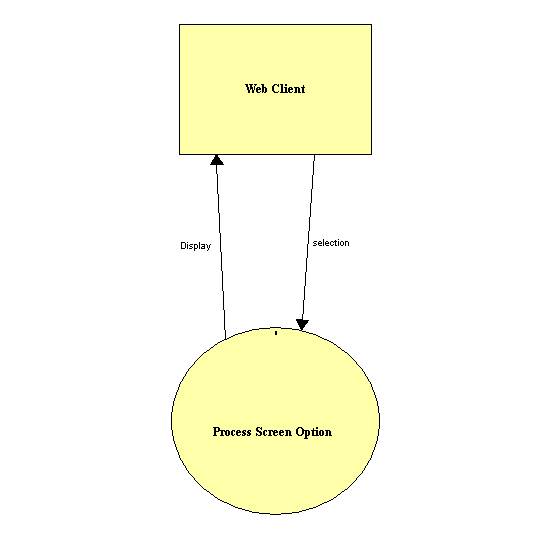
1.3 Detailed Data Flow Diagrams
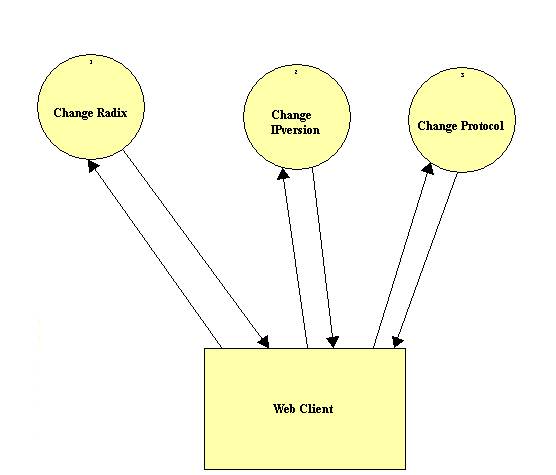
Level 0 Diagram:
Context Diagram:
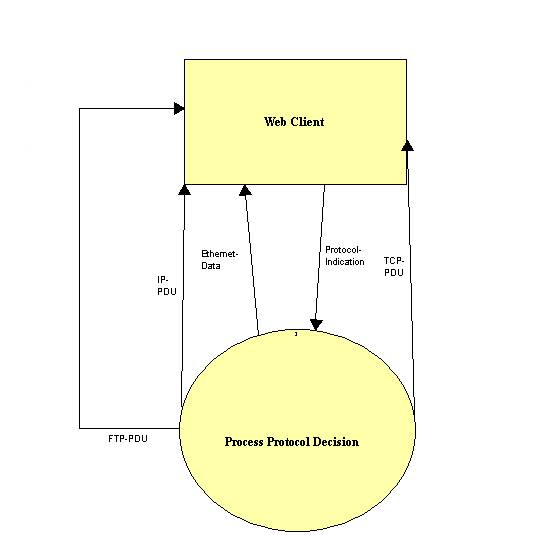
Detailed Diagram:
1.4 Hardware, Software and Human Interfaces
The prototype was developed and designed on Macromedia Fireworks,
a graphic design program.
The program will be written in HTML using Macromedia MX and
perhaps PHP (PHP Hypertext Processor) Version 4.1.2.
The TCP/IP Packet Descriptor program will be hosted as a web
site on the Siena College Computer Science Department’s Oraserv Linux server
(Red Hat version 7.1), running the Apache web server (version 1.3.19).
Any Netscape Navigator 7.x or greater and Internet Explorer
5.x or greater web browser may access the program.
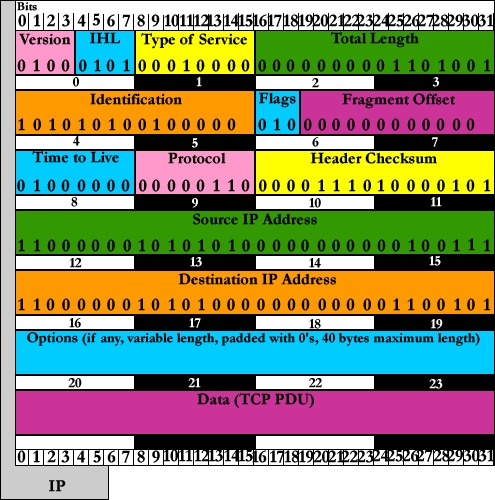
2.0 Architectural Design Specification
2.1 User Commands (AKA “Clickable Buttons”)
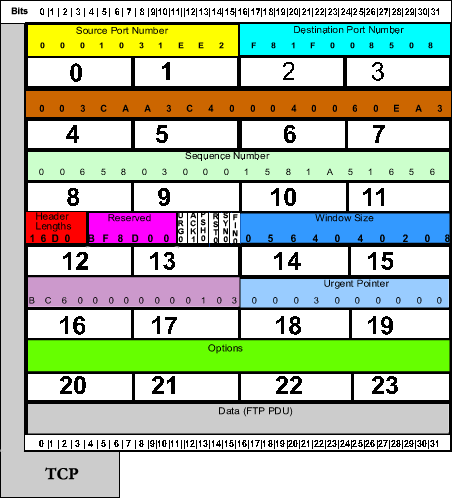
IP PDU
IP Version
Internet Header Length
Type of Service
Total Length of Ethernet Frame
Identification
Flags
Fragment Offset
Time to Live
Protocol
Header Checksum
Source IP Address
Destination IP Address
Options
Data
TCP PDU
Source Port Number
Destination Port Number
Sequence Number
Acknowledgement Number
Header Lengths
Reserved
Window Size
TCP Checksum
Urgent Pointer
Options
Data
2.2 Functional
Descriptions
2.2.1 IP PDU for the
selected FTP PDU
IP PDU
> IP Version for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: IP Version
Purpose and Definition: Version is a 4-bit field that indicates the
format of the internet header.
Field Key: 4
= IPv4
6
= IPv6
Data value (decimal): 4
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
4
|
|
Binary
|
0100
|
|
Decimal
|
4
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_IPVersion_FTP.
IP PDU > Internet Header Length for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name:
Internet Header Length
Purpose and Definition: The IHL field is a 4-bit field indicating
the length of the internet header in 32 bit words, and thus points to the
beginning of the data. The minimum
value of a correct header is 5.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value:
The value contained in our field is 20 bytes. This is the hexadecimal and decimal value of 5 multiplied by 4
bits.
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
5
|
Programming Hint: The name
for this variable in code will be IP_IHL_FTP.
IP PDU
> Type of Service for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name:
Type of Service
Purpose and Definition: Type of Service is an 8-bit field that
provides and indication of the abstract parameters of the quality of service
desired. These parameters guide the
selection of the actual service parameters when transmitting a datagram through
a particular network.
Field Key:
The major choice is a three-way tradeoff between low-delay,
high-reliability, and high-throughput.
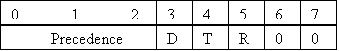
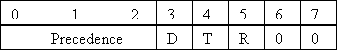
Bits 0-2: Precedence
Bit 3: (D) 0 =
Normal Delay 1 = Low Delay
Bit 4: (T) 0 =
Normal Throughput 1 = High
Throughput
Bit 5: (R) 0 =
Normal Reliability 1 = High
Reliability
Precedence:
111 =
Network Control 011
= Flash
110 =
Internetwork Control 010
= Immediate
101 =
CRITIC/ECP 001
= Priority
100 = Flash
Overrided 000 = Routine
Data value (hexadecimal): 10
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
16
|
Programming Hint: The name
for this variable in code will be IP_TypeOfService_FTP.
IP PDU
> Total Length of Ethernet Frame for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Total Length of Ethernet Frame
Purpose and Definition: Total Length is a
16-bit field that indicates the length of the frame, measured in octets,
including internet header and data. The
maximum size is 216-1 or 65,535 octets; however, the recommended
maximum size is 576 octets.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data values (hexadecimal): 69
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
6
|
9
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0110
|
1001
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
105
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
i
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TotalLength_FTP.
IP PDU > Identification for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Identification
Purpose and Definition: Identification is a 16-bit field. An identifying value is assigned by the
sender to aid in assembling the fragments of a datagram. The identifier is chosen based on the need
to provide a way to uniquely identify the fragments and protocol for the time
the datagram or any fragment could be alive in the internet.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): AA 41
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
A
|
A
|
4
|
1
|
|
Binary
|
1010
|
1010
|
0100
|
0001
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Idenfification_FTP.
IP PDU > Flags for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name:
Flags
Purpose and Definition: Flags is a 3-bit field that indicates
directions for fragmentation.
Field Key:
Bit 0: reserved, must be 0
Bit 1: (DF) 0 = May
Fragment 1 = Don’t Fragment
Bit 2: (MF) 0 = Last Fragment 1 = More Fragment
Data value (binary): 010
Data values in other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Flags_FTP.
IP PDU > Fragment Offset for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name:
Fragment Offset
Purpose and Definition: The Fragment Offset is a 13- bit field
indicating where in the Ethernet frame this fragment begins. The Fragment Offset is measured in units of
8 octets, and the first fragment has offset 0.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value (decimal): 0
Data values in other bases:
Binary: 0 0000 0000 0000
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_FragmentOffset_FTP.
IP PDU
> Time to Live for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Time to Live
Purpose and Definition: Time to Live is an 8-bit field that
indicates the maximum time the datagram is allowed to remain in the
internet. If this field contains the
value 0, then the datagram must be destroyed.
This field is modified in internet header processing. The time is measure in units of seconds, and
is set by the sender to the maximum time the datagram is allowed to be in the
internet. This field is decreased at
each point that the internet header is processed. The intention is to cause undeliverable packets to be discarded,
and to bind the maximum datagram lifetime.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value (decimal): 64
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
4
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0100
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
64
|
Programming Hint: The name
for this variable in code will be IP_TimeToLive_FTP.
IP PDU
> Protocol for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name:
Protocol
Purpose and Definition: Protocol is an 8-bit field that indicates
the next level protocol that is used in the data portion of the internet
diagram.
Field Key:
Dec Hex Protocol Dec Hex Protocol
0 00 Reserved 22 16 Multiplexing
1 01 ICMP 23 17 DCN
2 02 Unassigned 24 18
TAC Monitoring
3 03 Gateway-to-Gateway 25-76 19-4C Unassigned
4 04 CMCC
Gateway Monitoring Message 77 4D Any local network
5 05 ST 100 64 SATNET and Backroom
EXPAK
6 06 TCP 101 65 MIT Subnet Support
7 07 UCL 102-104 66-68
Unassigned
10 0A Unassigned 105 69
SATNET Monitoring
11 0B Secure 106 6A Unassigned
12 0C BBN
RCC Monitoring 107 6B Internet Packet
Core Utility
13 0D NVP 110-113 6E-71
Unassigned
14 0E PUP 114 72 Backroom
SATNET Monitoring
15 0F Pluribus 115 73
Unassigned
16 10 Telnet 116 74 WIDEBAND Monitoring
17 11 XNET 117 75 WIDEBAND EXPAK
20 14 Chaos 120-376 78-0178 Unassigned
21 15 User Datagram 377 0179 Reserved
Data value (hexadecimal): 06
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
6
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0110
|
|
Decimal
|
6
|
RFC Link: http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc790.html
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Protocol_FTP.
IP PDU > Header Checksum for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Header Checksum
Purpose and
Definition: The Header Checksum
is a 16-bit field. The Checksum is the
16-bit one’s complement sum of all 16-bit words in the header. For purposes of computing the checksum, the
initial value of its field is zero.
When both header checksums are equal, then the header bits are
correct. If either checksums vary, then
a new, correct packet will need to be sent.
This is a simple way to compute the checksum and
experimental evidence indicates that it is adequate, but it is provisional and
may be replaced by a CRC procedure, depending on further experience.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(hexadecimal): 0E 85
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
E
|
8
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
1110
|
1000
|
0101
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_HeaderChecksum_FTP.
IP PDU > Source
Address for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Source Address
Purpose and
Definition: The Source Address
is a 32-bit field that contains the IP address of the host that sent the IP
Packet.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(decimal): 192.168.0.39
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
C
|
0
|
A
|
8
|
0
|
0
|
2
|
7
|
|
Binary
|
1100
|
0000
|
1010
|
1000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0010
|
0111
|
|
Decimal
|
192
|
168
|
0
|
39
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_SourceAddress_FTP.
IP PDU > Destination Address for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Destination Address
Purpose and
Definition: The Destination
Address is a 32-bit field that contains the address of the host that is to
receive the data contained within the IP packet.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value
(decimal): 192.168.0.101
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
C
|
0
|
A
|
8
|
0
|
0
|
6
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
1100
|
0000
|
1010
|
1000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0110
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
192
|
168
|
0
|
101
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_DestinationAddress_FTP.
IP PDU > Options and Padding for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Options and Padding
Purpose and
Definition: The options may or
may not appear in Ethernet packets.
They must be implemented by all IP modules (host and gateways). What is optional is their transmission in
any particular packet, not their implementation.
The option field is variable in length. There may be zero or more options. There are two cases for the format of an
option.
Case 1: A
single octet of option type
Case 2: An
option-type octet, an option-length octet, and the actual option-data octets.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data values: Not applicable
Data values in
other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_OptionsPadding_FTP.
IP PDU > Data for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Data
Purpose and
Definition: The Data is a
variable length field which contains the actual data that is being sent from
one host to another. The data field may
start with a Layer 4 header, which will give additional instructions to the
application that will be receiving the data; alternately, it may be an ICMP
header and not contain any user data at all.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data values
(hexadecimal) : (TCP) 80 30 00
15 81 A5 16 6C 87 A3 53 5D 80 18 16 D0 11 F4 00 00 01 01 08 0A 1B 25 F3 A1 0b
DD 73 58
(FTP) 50 41 53 53 20 66 31 61 32 6B 33 75 73 65 72 0D 0A
Data values in
other bases:
Hexadecimal: (TCP) 0 x 80 30 00 15 81 A5 16 6C 87 A3 53 5D
80 18 16 D0 11 F4 00 00 01 01 08 0A 1B 25 F3 A1 0B DD 73 58
(FTP) 50 41 53 53 20 66 31 61 32 6B 33 75 73 65 72 0D 0A
ASCII: (TCP) ↑ 0 © © ↑ ↑ © ↑
↑ S ] ↑
© © ↑ © ↑ © © © © © © © % ↑
↑ © ↑ s X
(FTP) P A S S S © f 1 a 2 k 3 u s e r © ©
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Data_FTP.
2.2.2 TCP PDU for the
selected FTP PDU
IP > TCP PDU > Source Port for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Source Port
Purpose and
Definition:
This 16-bit number represents the name of the application
that sent the data in the IP packet.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(decimal): 32816
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
8
|
0
|
3
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
1000
|
0000
|
0011
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
128
|
48
|
|
ASCII
|
á
|
0
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_SourcePort_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Destination Port for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Destination Port
Purpose and
Definition:
This 16-bit number represents the name of the application that is to
receive the data contained within the IP packet. This is one of the major
differences between a Layer 3 and a Layer 4 header: the Layer 3 header contains
the IP address of the computer that is to receive the IP packet; once that
packet has been received, the port address in the Layer 4 header ensures that
the data contained within that IP packet is passed to the correct application
on that computer.
Field Key:
This key indicates
assigned port number values:
Dec Port Numbers
0 Reserved
1-32767 Internet registered ("well-known") protocols32768-98303 Reserved, to allow TCPv7-TCPv4 conversion
98304 & up Dynamic assignment
Data value
(decimal): 21 (indicates FTP)
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0001
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
21
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
Source: http://www.zvon.org/tmRFC/RFC1475/Output/chapter4.html
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_DestinationPort_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Sequence Number for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Sequence Number
Purpose and
Definition:
TCP is responsible for ensuring that all IP packets sent are actually
received. When an application's data is packaged into IP packets, TCP will give
each IP packet a sequence number. Once all the packets have arrived at the
receiving computer, TCP uses the number in this 32-bit field to ensure that all
of the packets actually arrived and are in the correct sequence.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value
(decimal): 2175080044
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
8
|
1
|
A
|
5
|
1
|
6
|
6
|
C
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0011
|
1100
|
1010
|
1010
|
0011
|
1100
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
60
|
176
|
60
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
‘
|
á
|
‘
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_SequenceNumber_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Acknowledgement Number for the selected FTP
PDU
Field Name: Acknowledgement
Number
Purpose and Definition:
This number is used by the receiving computer to acknowledge which
packets have successfully arrived. This number will be the sequence number of
the next packet the receiver is ready to receive.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value:
2275627869
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
8
|
7
|
A
|
3
|
5
|
3
|
5
|
D
|
|
Binary
|
1000
|
0111
|
1010
|
0011
|
0101
|
0011
|
0101
|
1101
|
|
Decimal
|
135
|
163
|
83
|
93
|
|
ASCII
|
á
|
á
|
S
|
]
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_AcknowledgementNumber_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Header Length or Offset for the selected
FTP PDU
Field Name: Header
Length or Offset
Purpose and Definition:
This is identical in concept to the header length in an IP packet,
except this time it indicates the length of the TCP header.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value (bytes): 32
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
8
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
1000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
128
|
|
ASCII
|
á
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_HeaderLength_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Reserved for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Reserved
Purpose and
Definition:
These 6 bits are unused and are always set to 0.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(binary): 0000 00
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_Reserved_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Control Flags for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Control Flags
Purpose and
Definition:
Every TCP packet contains this 6-bit value that indicates how many
octets it can receive at once. When IP packets are received, they are placed in
a temporary area of RAM known as a buffer until the receiving computer has a
chance to process them; this value represents how big a buffer the receiving
host has made available for this temporary storage of IP packets.
Field Key:
- Acknowledgement
(ACK)
- Push
(PSH)
- Reset
(RST)
- Synchronize
(SYN)
- Finish (FIN)
Data value
(binary): 01 1000
Data values in
other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_ControlFlags_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Window Size for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Window
Size
Purpose and
Definition:
Every TCP packet contains this 16-bit value that indicates how many
octets it can receive at once. When IP packets are received, they are placed in
a temporary area of RAM known as a buffer until the receiving computer has a
chance to process them; this value represents how big a buffer the receiving
host has made available for this temporary storage of IP packets.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value
(decimal): 5840
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
6
|
D
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
0110
|
1110
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
22
|
224
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
á
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_WindowSize_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Checksum for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Checksum
Purpose and Definition:
Unlike IP, TCP is responsible for ensuring that the entire IP packet
arrived intact. TCP will run a CRC on the entire IP packet (not just the
header) and place the resulting checksum in this field. When the IP packet is
received, TCP re-runs the CRC on the entire packet to ensure the checksum is
the same.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(hexadecimal): 11 F4
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
1
|
F
|
4
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
0001
|
1111
|
0100
|
|
Decimal
|
17
|
244
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_Checksum_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Urgent Pointer for the selected FTP PDU
Field Name: Urgent Pointer
Purpose and Definition:
If the Urgent flag is set to on, this value indicates where the urgent data is
located.
Information Key: Not
applicable
Data value: Not applicable
Data values in
other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_UrgentPointer_FTP.
IP > TCP PDU > Options and Padding for the selected FTP
PDU
Field Name: Options and Padding
Purpose and
Definition:
Like IP options, this field is optional and represents additional
instructions not covered in the other TCP fields. Again, if an option does not
fill up a 32-bit word, it will be filled in with padding bits.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value
(hexadecimal): 01 01 08 0A 1B 25 F3 A1 0B DD 73 58
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
8
|
0
|
A
|
1
|
B
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0001
|
0000
|
0001
|
0000
|
1000
|
0000
|
1010
|
0001
|
1011
|
|
Decimal
|
1
|
1
|
8
|
10
|
27
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
2
|
5
|
F
|
3
|
A
|
1
|
0
|
B
|
D
|
D
|
|
Binary
|
0010
|
0101
|
1111
|
0011
|
1010
|
0001
|
0000
|
1011
|
1101
|
1101
|
|
Decimal
|
37
|
243
|
161
|
11
|
221
|
|
ASCII
|
%
|
á
|
á
|
©
|
á
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
7
|
3
|
5
|
8
|
|
Binary
|
0101
|
0011
|
0101
|
1000
|
|
Decimal
|
115
|
96
|
|
ASCII
|
á
|
á
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_OptionsPadding_FTP.
2.2.3 FTP PDU for the selected FTP PDU
IP
>TCP > FTP PDU for the FTP Packet
RFC Link: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc0959.txt?number=959
PASS (Password)
The argument field is a Telnet string specifying the
user’s password. This command must be
immediately preceded by the user name command, and, for some sites, completes
the user’s identification for access control.
What is Contained in
the Packet
Request: PASS
Request Arg: f1a2k3user
Data Values
(hexadecimal): 50 41 53 53 20 66 31
61 32 6B 33 75 73 65 72 0D 0A
Data Values in Other
Bases
|
ASCII
|
P
|
A
|
S
|
S
|
SPC
|
f
|
1
|
a
|
2
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
5
0
|
4
1
|
5
3
|
5
3
|
2
0
|
6
6
|
3
1
|
6
1
|
3
2
|
|
Binary
|
0101 0000
|
0100 0001
|
0101 0011
|
0101 0011
|
0010 0000
|
0110 0110
|
0011 0001
|
0110 0001
|
0011 0010
|
|
Decimal
|
80
|
65
|
83
|
83
|
32
|
102
|
49
|
97
|
59
|
|
ASCII
|
k
|
3
|
u
|
s
|
e
|
r
|
\r
|
\n
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
6 B
|
3 3
|
7 5
|
7 3
|
6 5
|
7 2
|
0 D
|
0
A
|
|
Binary
|
0110 1011
|
0011 0011
|
0111 0101
|
0111 0011
|
0110 0101
|
0111 0010
|
0000 1101
|
0000 1010
|
|
Decimal
|
107
|
51
|
117
|
115
|
101
|
114
|
13
|
10
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TCP_FTP_PDU_FTP.
2.2.4 IP PDU for the selected ICMP PDU
IP PDU
> Version for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Version
Purpose and Definition: Version is a 4-bit field that indicates the
format of the internet header.
Field Key: 4
= IPv4
6
= IPv6
Data value (decimal): 4
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
4
|
|
Binary
|
0100
|
|
Decimal
|
4
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Version_ICMP.
IP PDU > Internet Header Length for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Internet Header Length
Purpose and Definition: The IHL field is a 4 bit field indicating
the length of the internet header in 32 bit words, and thus points to the
beginning of the data. The minimum
value of a correct header is 5.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value:
The value contained in our field is 20 bytes. This is the hexadecimal and decimal value of 5 multiplied by 4
bits.
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
5
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Version_ICMP.
IP PDU
> Type of Service for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Type of Service
Purpose and Definition: Type of Service is an 8-bit field that
provides and indication of the abstract parameters of the quality of service
desired. These parameters guide the
selection of the actual service parameters when transmitting a datagram through
a particular network.
Field Key:
The major choice is a three-way tradeoff between low-delay,
high-reliability, and high-throughput.
Bits 0-2: Precedence
Bit 3: (D) 0 =
Normal Delay 1 = Low Delay
Bit 4: (T) 0 =
Normal Throughput 1 = High
Throughput
Bit 5: (R) 0 =
Normal Reliability 1 = High
Reliability
Precedence:
111 =
Network Control 011
= Flash
110 =
Internetwork Control 010
= Immediate
101 =
CRITIC/ECP 001
= Priority
100 = Flash
Overrided 000 = Routine
Data value (hexadecimal): 00
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TypeOfService_ICMP.
IP PDU
> Total Length of Ethernet Frame for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Total Length of Ethernet Frame
Purpose and Definition: Total Length is a
16-bit field that indicates the length of the frame, measured in octets,
including internet header and data. The
maximum size is 216-1 or 65,535 octets; however, the recommended
maximum size is 576 octets.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data values (decimal): 84
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
5
|
4
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0101
|
0100
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
84
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
T
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_TotalLength_ICMP.
IP PDU
> Identification for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Identification
Purpose and Definition: Identification is a 16-bit field. An identifying value is assigned by the
sender to aid in assembling the fragments of a datagram. The identifier is chosen based on the need
to provide a way to uniquely identify the fragments and protocol for the time
the datagram or any fragment could be alive in the internet
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): 00 00
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Identification_ICMP.
IP PDU
> Flags for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Flags
Purpose and Definition: Flags is a 3-bit field that indicates
directions for fragmentation.
Field Key:
Bit 0: reserved, must be 0
Bit 1: (DF) 0 = May
Fragment 1 = Don’t Fragment
Bit 2: (MF) 0 = Last Fragment 1 = More Fragment
Data value (binary): 010
Data values in other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Flags_ICMP.
IP PDU > Fragment Offset
for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Fragment Offset
Purpose and Definition: The Fragment Offset is a 13- bit field
indicating where in the Ethernet frame this fragment begins. The Fragment Offset is measured in units of
8 octets, and the first fragment has offset 0.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value (decimal): 0
Data values in other bases:
Binary: 0 0000 0000 0000
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_FragmentOffset_ICMP.
IP PDU
> Time to Live for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Time to Live
Purpose and Definition: Time to Live is an 8-bit field that
indicates the maximum time the datagram is allowed to remain in the
internet. If this field contains the
value 0, then the datagram must be destroyed.
This field is modified in internet header processing. The time is measure in units of seconds, and
is set by the sender to the maximum time the datagram is allowed to be in the
internet. This field is decreased at
each point that the internet header is processed. The intention is to cause undeliverable packets to be discarded,
and to bind the maximum datagram lifetime.
Field Key:
Not applicable
Data value (decimal): 64
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
4
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0100
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
64
|
Programming Hint: The name for this variable in code will be
IP_TimeToLive_ICMP.
IP PDU > Protocol for the
selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Protocol
Purpose and Definition: Protocol is an 8-bit field that indicates
the next level protocol that is used in the data portion of the internet
diagram.
Field Key:
Dec Hex Protocol Dec Hex Protocol
0 00 Reserved 22 16 Multiplexing
1 01 ICMP 23 17 DCN
2 02 Unassigned 24 18 TAC Monitoring
3 03 Gateway-to-Gateway 25-76 19-4C Unassigned
4 04 CMCC
Gateway Monitoring Message 77 4D Any local network
5 05 ST 100 64 SATNET and Backroom
EXPAK
6 06 TCP 101 65 MIT Subnet Support
7 07 UCL 102-104 66-68
Unassigned
10 0A Unassigned 105 69 SATNET Monitoring
11 0B Secure 106 6A Unassigned
12 0C BBN
RCC Monitoring 107 6B Internet Packet Core Utility
13 0D NVP 110-113 6E-71
Unassigned
14 0E PUP 114 72 Backroom
SATNET Monitoring
15 0F Pluribus 115 73 Unassigned
16 10 Telnet 116 74 WIDEBAND Monitoring
17 11 XNET 117 75 WIDEBAND EXPAK
20 14 Chaos 120-376 78-0178 Unassigned
21 15 User Datagram 377 0179 Reserved
Data value (hexadecimal): 01
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
6
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0001
|
|
Decimal
|
1
|
RFC Link: http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc790.html
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_Protocol_ICMP.
IP PDU > Header
Checksum for the Selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Header Checksum
Purpose and
Definition: The Header Checksum
is a 16-bit field. This CRC algorithm
is the 16-bit one’s complement sum of all the 16-bit words in the header. For purposes of computing the checksum, the
value of the checksum field is initially zero.
When both header checksums are the same, then the header bits are
correct. If either checksums vary, then
a packet will need to be resent.
This is a simple way to compute the checksum and
experimental evidence indicates that it is adequate, but it is provisional and
may be replaced by a CRC procedure, depending on further experience.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value (hexadecimal):
B8 CC
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
B
|
8
|
C
|
C
|
|
Binary
|
1011
|
1000
|
1100
|
1100
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_HeaderChecksum_ICMP.
IP PDU > Source
Address for the Selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Source Address
Purpose and
Definition: The Source Address
is a 32-bit field that contains the IP address of the host that sent the IP
Packet.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value: 192.168.0.39
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
C
|
0
|
A
|
8
|
0
|
0
|
2
|
7
|
|
Binary
|
1100
|
0000
|
1010
|
1000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0010
|
0111
|
|
Decimal
|
192
|
168
|
0
|
39
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_SourceAddress_ICMP.
IP PDU > Destination
Address for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Destination Address
Purpose and Definition: The Destination Address is a 32-bit field
that contains the address of the host that is to receive the data contained
within the IP packet.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data value: 192.168.0.101
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
C
|
0
|
A
|
8
|
0
|
0
|
6
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
1100
|
0000
|
1010
|
1000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0110
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
192.
|
168.
|
0.
|
101
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_DestinationAddress_ICMP.
IP PDU > Options and Padding for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Options and Padding
Purpose and
Definition: The options may or
may not appear in Ethernet packets.
They must be implemented by all IP modules (host and gateways). What is optional is their transmission in
any particular packet, not their implementation.
The option field is variable in length. There may be zero or more options. There are two cases for the format of an
option.
Case 1: A
single octet of option type
Case 2: An
option-type octet, an option-length octet, and the actual option-data octets.
Field Key: Not
applicable
Data values: Not applicable
Data values in
other bases: Not applicable
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_OptionsPadding_ICMP.
2.2.5 ICMP PDU for the selected ICMP PDU
IP > ICMP Header > Type for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Type
Purpose and Definition: The type is an 8-bit field that identifies
what sort of message the ICMP protocol is sending.
Field Key:
Dec Hex Message Type Dec
Hex Message Type
0 00 Echo
Reply 16
10 Information Reply
1 01 Unassigned 17
11 Address Mask Request
2 02 Unassigned 18
12 Address Mask Reply
3 03 Destination
Unreachable 19
13 Reserved (for Security)
4 04 Source
Quench 20-29
14-1D Reserved (for Robustness
Experiment)
5 05 Redirect 30
1E Traceroute
6 06 Alternate
Host Address 31
1F Datagram Conversion Error
7 07 Unassigned 32
20 Mobile Host Redirect
8 08 Echo 33
21 IPv6 Where-Are-You
9 09 Router
Advertisement 34
22 IPv6 I-Am-Here
10 0A Router
Solicitation 35
23 Mobile Registration Request
11 0B Time
Exceeded 36
24 Mobile Registration Reply
12 0C Parameter
Problem 37
25 Domain Name Request
13 0D Timestamp 38
26 Domain Name Reply
14 0E Timestamp
Reply 39
27 SKIP
15 0F Information
Request 40
28 Photuris
41-255 29-FF
Reserved
Data value: 8 (Echo (ping) Request)
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
8
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
1000
|
|
Decimal
|
8
|
RFC Link: http://www.iana.org/assignments/icmp-parameters
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Type_ICMP.
IP > ICMP Header > Code for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name: Code
Purpose and
Definition: Code is an 8-bit field that provides further information
about the associated type field.
Field Key:
Type Name Type Name
0 Echo Reply (used by “PING”) 7 Unassigned
0 No Code 8 Echo (used by "PING")
1 Unassigned 0 No Code
2 Unassigned 9 Router Advertisement
3 Destination Unreachable 0 No Code
0 Net Unreachable 10 Router Selection
1 Host Unreachable 0 No Code
2 Protocol Unreachable 11 Time Exceeded
3 Port Unreachable 0 Time to Live exceeded in Transit
4 Fragmentation needed and 1 Fragment Reassembly Time Exceeded
Don't Fragment was Set 12 Parameter Problem
5 Source Route Failed 0 Pointer indicates the error
6 Destination Network Unknown 1 Missing a Required Option
7 Destination Host Unknown 2 Bad Length
8 Source Host Isolated 13 Timestamp
9 Communication with Destination 0 No Code
Network is Administratively Prohibited 14 Timestamp Reply
10 Communication with Destination 0 No Code
Host is Administratively Prohibited 15 Information Request
11 Destination Network Unreachable 0 No Code
for Type of Service 16 Information Reply
12 Destination Host Unreachable for 0 No Code
Type of Service 17 Address Mask Request
4 Source Quench 0 No Code
0 No Code 18 Address Mask Reply
5 Redirect 0 No Code
0 Redirect Datagram for the Network 19 Reserved (for Security)
1 Redirect Datagram for the Host 20-29 Reserved (for Robustness Experiment)
2 Redirect Datagram for the Type of 30 Traceroute
Service and Network 31 Datagram Conversion Error
3 Redirect Datagram for the Type of 32 Mobile Host Redirect
Service and Host 33 IPv6 Where-Are-You
6 Alternate Host Address 34 IPv6 I-Am-Here
0 Alternate Address for Host 35 Mobile Registration Request
36 Mobile Registration Reply
Data value (decimal): 0
Data values in
other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Header_ICMP.
IP > ICMP Header > Checksum for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Checksum
Purpose and Definition: The checksum is the 16-bit one’s complement
of the one’s complement sum of the ICMP message, starting with the ICMP
type. For computing the checksum, the
checksum field should initially be zero.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): C9 15
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
C
|
9
|
1
|
5
|
|
Binary
|
1100
|
1001
|
0001
|
0101
|
|
Decimal
|
201
|
21
|
|
ASCII
|
á
|
©
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Checksum_ICMP.
IP > ICMP Header > Identifier for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Identifier
Purpose and Definition: The identifier is a 16-bit field that is used in matching echoes and replies for when the code field is zero.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): 70 60
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
7
|
0
|
6
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0111
|
0000
|
0110
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
112
|
96
|
|
ASCII
|
P
|
‘
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Identifier_ICMP.
IP > ICMP Header > Sequence for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Sequence
Purpose and Definition: The sequence is a 16-bit field that is used in matching echoes and replies for when the code field is zero.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): 70 60
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
0
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
Programming Hint:
The name for this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Sequence_ICMP.
IP > ICMP Header > Data for the selected ICMP PDU
Field Name:
Data
Purpose and Definition: The data is a variable-length field that contains the actual information that is sent in the ping packet.
Field Key: Not applicable
Data value (hexadecimal): 42 B1 89 3F 00 00 00
00 2C C6 07 00 00 00 00 00 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2A 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
Data values in other bases:
|
Hexadecimal
|
4
|
2
|
B
|
1
|
8
|
9
|
3
|
F
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0100
|
0010
|
1011
|
0001
|
1000
|
1001
|
0011
|
1111
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
66
|
177
|
137
|
63
|
0
|
|
ASCII
|
B
|
á
|
á
|
?
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
2
|
C
|
C
|
6
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0010
|
1100
|
1100
|
0110
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
44
|
198
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
,
|
á
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
7
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0111
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
0000
|
|
Decimal
|
7
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
1
|
3
|
|
Binary
|
0000
|
0000
|
0001
|
0000
|
0001
|
0001
|
0001
|
0010
|
0001
|
0011
|
|
Decimal
|
0
|
16
|
17
|
18
|
19
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
4
|
1
|
5
|
1
|
6
|
1
|
7
|
1
|
8
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
0100
|
0001
|
0101
|
0001
|
0110
|
0001
|
0111
|
0001
|
1000
|
|
Decimal
|
20
|
21
|
22
|
23
|
24
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
9
|
1
|
A
|
1
|
B
|
1
|
C
|
1
|
D
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
1001
|
0001
|
1010
|
0001
|
1011
|
0001
|
1100
|
0001
|
1101
|
|
Decimal
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
29
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
©
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
1
|
E
|
1
|
F
|
2
|
0
|
2
|
1
|
2
|
2
|
|
Binary
|
0001
|
1110
|
0001
|
1111
|
0010
|
0000
|
0010
|
0001
|
0010
|
0010
|
|
Decimal
|
30
|
31
|
32
|
33
|
34
|
|
ASCII
|
©
|
©
|
SPACE
|
!
|
“
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
2
|
3
|
2
|
4
|
2
|
5
|
2
|
6
|
2
|
7
|
|
Binary
|
0010
|
0011
|
0010
|
0100
|
0010
|
0101
|
0010
|
0110
|
0010
|
0111
|
|
Decimal
|
35
|
36
|
37
|
38
|
39
|
|
ASCII
|
#
|
$
|
%
|
&
|
‘
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
2
|
8
|
2
|
9
|
2
|
A
|
2
|
B
|
2
|
C
|
|
Binary
|
0010
|
1000
|
0010
|
1001
|
0010
|
1010
|
0010
|
1011
|
0010
|
1100
|
|
Decimal
|
40
|
41
|
42
|
43
|
44
|
|
ASCII
|
(
|
)
|
*
|
+
|
,
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
2
|
D
|
2
|
E
|
2
|
F
|
3
|
0
|
3
|
1
|
|
Binary
|
0010
|
1101
|
0010
|
1110
|
00010
|
1111
|
0011
|
0000
|
0011
|
0001
|
|
Decimal
|
45
|
46
|
47
|
48
|
49
|
|
ASCII
|
-
|
.
|
/
|
0
|
1
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
3
|
2
|
3
|
3
|
3
|
4
|
3
|
5
|
3
|
6
|
|
Binary
|
0011
|
0010
|
0011
|
0011
|
0011
|
0100
|
0011
|
0101
|
0011
|
0110
|
|
Decimal
|
50
|
51
|
52
|
53
|
54
|
|
ASCII
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
|
Hexadecimal
|
3
|
7
|
|
Binary
|
0011
|
0111
|
|
Decimal
|
55
|
|
ASCII
|
7
|
Programming Hint: The name for
this variable in code will be IP_ICMP_Data_ICMP.
3.0 Appendix
3.1 Glossary
ASCII:
American Standard Code for
Information Interchange: a
code for representing English characters as numbers, with each letter assigned
a number from 0 to 127.
Attribute:
A named value or relationship that exists for some or all
instances of some entity and is directly associated with that instance.
Binary:
Pertaining to a number system that has just two unique
digits, 0 and 1. Computers operate on a
binary number system.
Code:
The symbolic
arrangement of data or instructions in a computer program or the set of such
instructions.
Data Flow
Diagram:
A graphical
notation used to describe how data flows between processes in a system. They are a representation of the functional
decomposition of a system.
Decimal:
Refers to numbers in base 10—the
numbers we use in everyday life.
Dynamic Combo
Menu:
Menu showing all actions possible at
the current moment.
Frame:
A feature that divides a
browser’s window into separate segments that can be scrolled independently of
each other; a single step in a sequence of programmed instructions
GUI:
Graphical User Interface: A user interface based on
graphics (icons, pictures, and menus) instead of text; uses a mouse as well as
a keyboard as an input device.
Gantt Chart:
A chart that
depicts progress in relation to time, often used in planning and tracking a
project
HTML:
Hypertext Transfer Markup Language: A markup language
used to structure text and multimedia documents and to set up hypertext links
between documents, used extensively on the World Wide Web.
Hexadecimal:
Refers to the base-16 number system which consists of 16
unique symbols: the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F.
Hypertext:
A
computer-based text retrieval system that enables a user to access particular
locations in web pages or other electronic documents by clicking on links
within specific web pages or documents.
Internet:
An
interconnected system of networks that connects computers around the world via
the TCP/IP protocol.
Linear Sequential Model:
Sometimes
called the classic life cycle or the waterfall model, this model suggests a
systematic, sequential approach to software development that begins at the
system level and progresses through analysis, design, coding, testing, and
support.
Linux:
A trademark for an open-source
version of the UNIX operating system.
Network:
A group of two
or more computer systems linked together.
Open-Source:
A method and
philosophy for software licensing and distribution designed to encourage use
and improvement of software written by volunteers by ensuring that anyone can
copy the source code.
PHP:
PHP Hypertext Preprocessor (server-side
scripting language)
Packet:
A short block of
data transmitted in a packet switching network.
PDU:
Protocol Data Unit: A packet of data passed across a
network.
Protocol:
A set of formal rules describing how to
transmit data, especially across a network.
Prototype:
An original type, form, or
instance serving as a basis or standard for later stages.
RFC:
Request for Comments: One of a long-establish series of numbered
Internet informational documents and standards widely followed by commercial
software and freeware in the Internet and Unix communities.
Software:
The code
executed by a computer, as opposed to the physical device which they run on.
TCP/IP:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol: A suite of protocols for communication
between computers, used as a standard for transmitting data over networks and
as the basis for standard Internet protocols.
UNIX:
A powerful
operating system developed at the ATT Bell Laboratories.
Use Case:
The
specification of sequences of actions that a system, subsystem, or class can
perform by interacting with outside actors.
Visible Analyst:
Project management software
used in Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) to create such illustrations
as the data flow diagrams.
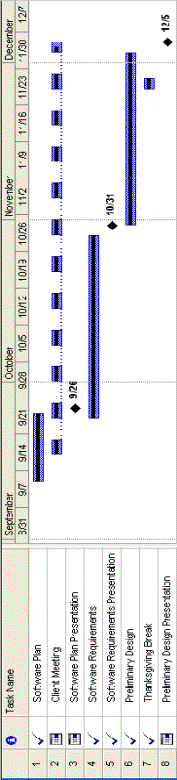
3.2 Gantt Charts
Fall Gantt Chart:
Yearlong Gantt Chart: